Integration with Argo CD
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool, which allows developers to define and control deployment of Kubernetes application resources from within their existing Git workflow. By integrating Open Cluster Management (OCM) with Argo CD, it enables both automation and greater flexibility managing Argo CD Applications across a large number of OCM managed clusters.
In this article, we want to show you how to integrate Argo CD with OCM and deploy application to OCM managed clusters by leveraging the Placement API, which supports multi-cluster scheduling.
Before starting with the following steps, we suggest you understand the content below:
- Argo CD ApplicationSet. It adds Application automation and seeks to improve multi-cluster support and cluster multitenant support within Argo CD.
- OCM Placement API. It is used to dynamically select a set of ManagedClusters in one or multiple ManagedClusterSets so that the workloads can be deployed to these clusters.
The first half of the KubeCon NA 2022 - OCM Multicluster App & Config Management also covers the integration with ArgoCD.
How it works
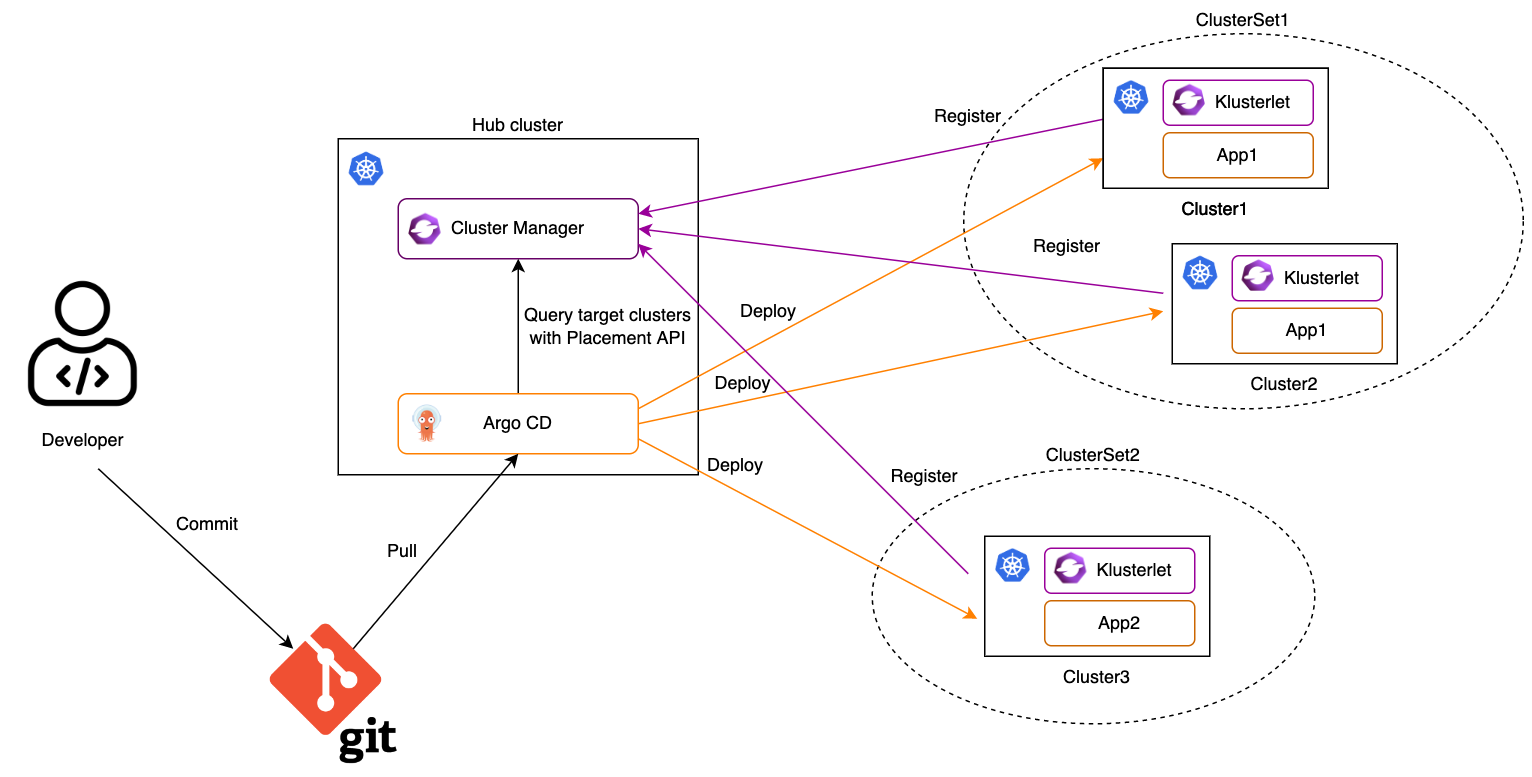
1. Import Kubernetes clusters to the OCM hub as managed clusters and organize them with managed clustersets.
2. Register the OCM managed clusters to ArgoCD.
The OCM managed clusters can be registered to Argo CD one by one manually by using Argo CD CLI. It may take time to finish it if there are a large number of clusters. In order to make the cluster registration easier, consider to use multicloud-integrations to automate the procedure.
3. Create a configuration of Cluster Decision Resource generator by using OCM Placement API.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: ocm-placement-generator
namespace: argocd
data:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: placementdecisions
statusListKey: decisions
matchKey: clusterName
EOF
With reference to this generator, an ApplicationSet can target the application to the clusters listed in the status of a set of PlacementDecision, which belong to a certain Placement.
4. Grant Argo CD permissions to access OCM resources.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: ocm-placement-consumer
namespace: argocd
rules:
- apiGroups: ["cluster.open-cluster-management.io"]
resources: ["placementdecisions"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: ocm-placement-consumer:argocd
namespace: argocd
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: ocm-placement-consumer
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: argocd
name: argocd-applicationset-controller
EOF
5. Bind at least one managed clusterset to the argocd namespace.
For example, in order to bind the global managed clusterset to the argocd namespace, the user must have an RBAC rule to create on the virtual subresource of managedclustersets/bind of the global managed clusterset.
clusteradm clusterset bind global --namespace argocd
The above command will create a ManagedClusterSetBinding resource in the argocd namespace. Normally, it should not be included by an application in the git repo because applying it to a Kubernetes cluster needs additional permissions.
6. Create a placement in the argocd namespace to select some managed clusters.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: Placement
metadata:
name: guestbook-app-placement
namespace: argocd
spec:
numberOfClusters: 10
EOF
7. Create an ApplicationSet in the argocd namespace.
The ApplicationSet has references to the Cluster Decision Resource generator previously created and placement. This will help Argo CD to determine where the application should be deployed. The managed clusters selected by the referenced placement may be changed dynamically. By setting requeueAfterSeconds of the generator in the ApplicationSet spec, the Argo CD will check the cluster decisions of the referenced placement periodically and ensure the application is deployed to the correct managed clusters.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: guestbook-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
generators:
- clusterDecisionResource:
configMapRef: ocm-placement-generator
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/placement: guestbook-app-placement
requeueAfterSeconds: 30
template:
metadata:
name: '{{clusterName}}-guestbook-app'
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: 'https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git'
targetRevision: HEAD
path: guestbook
destination:
name: '{{clusterName}}'
namespace: guestbook
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
EOF
8. Check the status of the ApplicationSet and the Application.
Confirm the ApplicationSet is created and an Application is generated for each selected managed cluster.
$ kubectl -n argocd get applicationsets
NAME AGE
guestbook-app 4s
$ kubectl -n argocd get applications
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
cluster1-guestbook-app Synced Progressing
cluster2-guestbook-app Synced Progressing
And on each selected managed cluster confirm the Application is running.
$ kubectl -n guestbook get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
guestbook-ui-6b689986f-cdrk8 1/1 Running 0 112s
What’s next
To build an OCM environment integrated with Argo CD with KinD clusters, see Deploy applications with Argo CD for more details.