This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Cluster Inventory
- 1: ClusterClaim
- 2: ManagedCluster
- 3: ManagedClusterSet
1 - ClusterClaim
What is ClusterClaim?
ClusterClaim is a cluster-scoped API available to users on a managed cluster it allows users to define key-value metadata on managed clusters.
These objects are collected by the klusterlet agent and synchronized to the status.clusterClaims field of the corresponding ManagedCluster object on the hub cluster. This mechanism enables centralized inventory management and property-based cluster filtering across your fleet.
Usage
ClusterClaim is used to specify additional properties of the managed cluster like
the clusterID, version, vendor and cloud provider. We defined some reserved ClusterClaims
like id.k8s.io which is a unique identifier for the managed cluster.
ClusterClaim Types and Collection Rule
There are two types of ClusterClaims collected from managed clusters.
-
Reserved ClusterClaimsare system defined claims with predefined names that identify fundamental cluster attributes (e.g., id.k8s.io for cluster ID, kubeversion.open-cluster-management.io for Kubernetes version). These are automatically populated. -
Custom ClusterClaimsare user-defined claims for custom metadata (e.g., environment, cost-center, compliance-tier).
Collection Behavior
All ClusterClaims are reported to the hub except when.
-
The
ClusterClaimwith the labelopen-cluster-management.io/spoke-onlywill not be synced to the status ofManagedCluster. -
Only a limited number of custom claims are synchronized (default: 20). Excess claims are truncated.
In addition to the reserved ClusterClaims, users can also customize 20 ClusterClaims by default.
The maximum count of customized ClusterClaims can be configured via the flag
max-custom-cluster-claims of registration agent on the managed cluster.
Configuring ClusterClaims via Klusterlet API
The collection and naming of ClusterClaims can now be configured directly through the Klusterlet API, providing declarative control over claim management.
API Configuration Structure
apiVersion: operator.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: Klusterlet
spec:
clusterClaimConfiguration:
# Maximum number of custom ClusterClaims allowed (default: 20)
maxCustomClusterClaims: 50
# Custom suffixes for reserved ClusterClaim names
reservedClusterClaimSuffixes:
- "mycompany.com"
Configuration Options
-
maxCustomClusterClaims(integer, default: 20) controls the maximum number of custom ClusterClaims synchronized to the hub. Increase this value if your environment requires reporting more than 20 custom attributes per cluster. -
reservedClusterClaimSuffixes(array of strings) specifies custom suffixes to identify additional reserved claims. Claims matching these suffixes are treated as reserved claims. For example, ifreservedClusterClaimSuffixesis set tomycompany.com, claims likeid.mycompany.com,name.mycompany.com, andanything.mycompany.comwill be treated as reserved.
Example
1. Creating a Reserved ClusterClaim
Here is a ClusterClaim example specifying a id.k8s.io:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: id.k8s.io
spec:
value: myCluster
2. Creating Custom Cluster Claims
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: claim-1
spec:
value: "custom-claim-1"
---
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: claim-2
spec:
value: "custom-claim-2"
3. Spoke-Only ClusterClaim (Not Synced)
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: claim-3
annotations:
open-cluster-management.io/spoke-only: "true"
spec:
value: "custom-claim-3"
4. Using Custom Reserved ClusterClaim Suffixes
You can configure custom suffixes to treat specific ClusterClaims as reserved. This is useful when you want to define organization-specific reserved claims.
First, configure the Klusterlet with your custom suffix:
apiVersion: operator.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: Klusterlet
spec:
clusterClaimConfiguration:
reservedClusterClaimSuffixes:
- "mycompany.com"
Then create ClusterClaims using your custom suffix:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: id.mycompany.com
spec:
value: id
---
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: name.mycompany.com
spec:
value: name
---
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterClaim
metadata:
name: region.mycompany.com
spec:
value: region
These claims will be treated as reserved claims and will not count against the maxCustomClusterClaims limit.
5. Viewing ClusterClaims on the Hub
After applying the ClusterClaim above to any managed cluster, the value of the ClusterClaim
is reflected in the ManagedCluster on the hub cluster:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ManagedCluster
metadata: ...
spec: ...
status:
clusterClaims:
- name: id.k8s.io
value: myCluster
- name: claim-1
value: custom-claim-1
- name: claim-2
value: custom-claim-2
- name: id.mycompany.com #Treated as a reserved claim
value: id
- name: name.mycompany.com #Treated as a reserved claim
value: name
- name: region.mycompany.com #Treated as a reserved claim
value: region
About-API Support in Open Cluster Management
Open Cluster Management (OCM) supports the use of ClusterProperty via the
about-api,
which allows administrators to define and expose cluster-scoped properties. These properties are
synced to the managed cluster’s ManagedCluster status and can coexist with
ClusterClaim but take precedence if a same-named property exists.
Enabling the Feature
To enable the ClusterProperty feature on the spoke cluster, the ClusterProperty feature gate must be
set on the Klusterlet component. This can be done by setting the feature gate in the Klusterlet configuration:
featureGates:
ClusterProperty: "true"
Ensure that the feature gate is enabled appropriately based on your cluster management strategy.
Using ClusterProperty
Creating a ClusterProperty
Cluster administrators can create a ClusterProperty custom resource in the spoke cluster. The following
is an example YAML for creating a ClusterProperty:
apiVersion: about.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterProperty
metadata:
name: example-property
spec:
value: "example-value"
Once created, the ClusterProperty will be automatically synced to the hub cluster and reflected within
the ManagedCluster resource’s status.
Syncing Existing Properties
After enabling the feature, any existing ClusterProperty resources will be synced to the ManagedCluster
status on the hub cluster.
Example: If example-property with value example-value already exists on the spoke cluster, its value
will populate into the ManagedCluster as:
status:
clusterClaims:
- name: "example-property"
value: "example-value"
Handling Conflicts with ClusterClaim
In case a ClusterClaim resource with the same name as a ClusterProperty exists, the ClusterProperty
will take precedence and the corresponding ClusterClaim will be ignored.
Updating ClusterProperties
Updating the value of an existing ClusterProperty will automatically reflect the change in the managed
cluster’s status:
spec:
value: "updated-value"
Deleting ClusterProperties
When a ClusterProperty is deleted from the spoke cluster, its corresponding entry in the ManagedCluster
status is removed:
kubectl delete clusterproperty example-property
This will result in the removal of the example-property from the ManagedCluster status on the hub cluster.
Additional Notes
- Both
ClusterPropertyandClusterClaimcan co-exist, withClusterPropertytaking precedence in naming conflicts. - The feature uses the existing OCM infrastructure for status synchronization, ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
- Ensure compatibility and testing in your environment before enabling the
ClusterPropertyfeature gate in production settings.
2 - ManagedCluster
What is ManagedCluster?
ManagedCluster is a cluster scoped API in the hub cluster representing the
registered or pending-for-acceptance Kubernetes clusters in OCM. The
klusterlet agent
working in the managed cluster is expected to actively maintain/refresh the
status of the corresponding ManagedCluster resource on the hub cluster.
On the other hand, removing the ManagedCluster from the hub cluster indicates
the cluster is denied/exiled from the hub cluster. The following is the
introduction of how the cluster registration lifecycle works under the hood:
Cluster registration and acceptance
Bootstrapping registration
Firstly, the cluster registration process should be initiated by the registration agent which requires a bootstrap kubeconfig e.g.:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: bootstrap-hub-kubeconfig
namespace: open-cluster-management-agent
type: Opaque
data:
kubeconfig: <base64-encoded kubeconfig>
A minimal RBAC permission required for the subject in the bootstrap kubeconfig will be:
CertificateSigningRequest’s “get”, “list”, “watch”, “create”, “update”.ManagedCluster’s “get”, “list”, “create”, “update”
Note that ideally the bootstrap kubeconfig is supposed to live for a short time (hour-ish) after being signed by the hub cluster so that it won’t be abused by unwelcome clients.
Last but not least, you can always live an easier life by leveraging OCM’s
command-line tool clusteradm to manage the whole registration process.
Approving registration
When we’re registering a new cluster into OCM, the registration agent will be
starting by creating an unaccepted ManagedCluster into the hub cluster along
with a temporary CertificateSigningRequest (CSR)
resource. The cluster will be accepted by the hub control plane, if the
following requirements are met:
- The CSR is approved and signed by any certificate provider setting filling
.status.certificatewith legit X.509 certificates. - The
ManagedClusterresource is approved by setting.spec.hubAcceptsClientto true in the spec.
Note that the cluster approval process above can be done by one-line:
$ clusteradm accept --clusters <cluster name>
Upon the approval, the registration agent will observe the signed certificate and persist them as a local secret named “hub-kubeconfig-secret” (by default in the “open-cluster-management-agent” namespace) which will be mounted to the other fundamental components of klusterlet such as the work agent. In a word, if you can find your “hub-kubeconfig-secret” successfully present in your managed cluster, the cluster registration is all set!
Overall the registration process in OCM is called double opt-in mechanism,
which means that a successful cluster registration requires both sides of
approval and commitment from the hub cluster and the managed cluster. This
will be especially useful when the hub cluster and managed clusters are
operated by different admins or teams. In OCM, we assume the clusters are
mutually untrusted in the beginning then set up the connection between them
gracefully with permission and validity under control.
Note that the functionality mentioned above are all managed by OCM’s registration sub-project, which is the “root dependency” in the OCM world. It includes an agent in the managed cluster to register to the hub and a controller in the hub cluster to coordinate with the agent.
Cluster heartbeats and status
By default, the registration will be reporting and refreshing its healthiness
state to the hub cluster on a one-minute basis, and that interval can be easily
overridden by setting .spec.leaseDurationSeconds on the ManagedCluster.
In addition to that, a few commonly-used information will also be reflected
in the status of the ManagedCluster, e.g.:
status:
version:
kubernetes: v1.20.11
allocatable:
cpu: 11700m
ephemeral-storage: "342068531454"
hugepages-1Gi: "0"
hugepages-2Mi: "0"
memory: 17474228Ki
pods: "192"
capacity:
cpu: "12"
ephemeral-storage: 371168112Ki
hugepages-1Gi: "0"
hugepages-2Mi: "0"
memory: 23777972Ki
pods: "192"
conditions: ...
Cluster taints and tolerations
To support filtering unhealthy/not-reporting clusters and keep workloads from being placed in unhealthy or unreachable clusters, we introduce the similar concept of taint/toleration in Kubernetes. It also allows user to add a customized taint to deselect a cluster from placement. This is useful when the user wants to set a cluster to maintenance mode and evict workload from this cluster.
In OCM, Taints and Tolerations work together to allow users to control the selection of managed clusters more flexibly.
Taints of ManagedClusters
Taints are properties of ManagedClusters, they allow a Placement to repel a set of ManagedClusters. A Taint includes the following fields:
- Key (required). The taint key applied to a cluster. e.g. bar or foo.example.com/bar.
- Value (optional). The taint value corresponding to the taint key.
- Effect (required). The Effect of the taint on Placements that do not
tolerate the taint. Valid effects are
NoSelect. It means Placements are not allowed to select a cluster unless they tolerate this taint. The cluster will be removed from the placement decision if it has already been selected by the Placement.PreferNoSelect. It means the scheduler tries not to select the cluster, rather than prohibiting Placements from selecting the cluster entirely. (This is not implemented yet, currently clusters with effectPreferNoSelectwill always be selected.)NoSelectIfNew. It means Placements are not allowed to select the cluster unless: 1) they tolerate the taint; 2) they have already had the cluster in their cluster decisions;
- TimeAdded (required). The time at which the taint was added. It is set automatically and the user should not to set/update its value.
Builtin taints to reflect the status of ManagedClusters
There are two builtin taints, which will be automatically added to ManagedClusters, according to their conditions.
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/unavailable. The taint is added to a ManagedCluster when it is not available. To be specific, the cluster has a condition ‘ManagedClusterConditionAvailable’ with status of ‘False’. The taint has the effectNoSelectand an empty value. Example,apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1 kind: ManagedCluster metadata: name: cluster1 spec: hubAcceptsClient: true taints: - effect: NoSelect key: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/unavailable timeAdded: '2022-02-21T08:11:54Z'cluster.open-cluster-management.io/unreachable. The taint is added to a ManagedCluster when it is not reachable. To be specific,-
- The cluster has no condition ‘ManagedClusterConditionAvailable’;
-
- Or the status of condition ‘ManagedClusterConditionAvailable’ is
‘Unknown’;
The taint has the effect
NoSelectand an empty value. Example,
- Or the status of condition ‘ManagedClusterConditionAvailable’ is
‘Unknown’;
The taint has the effect
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1 kind: ManagedCluster metadata: name: cluster1 spec: hubAcceptsClient: true taints: - effect: NoSelect key: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/unreachable timeAdded: '2022-02-21T08:11:06Z'-
Tolerations of Placements
Tolerations are applied to Placements, and allow Placements to select ManagedClusters with matching taints. Refer to Placement Taints/Tolerations to see how it is used for cluster selection.
Cluster removal
A previously registered cluster can opt-out cutting off the connection from either hub cluster or managed cluster. This is helpful for tackling emergency problems in your OCM environment, e.g.:
- When the hub cluster is overloaded, under emergency
- When the managed cluster is intended to detach from OCM
- When the hub cluster is found sending wrong orders to the managed cluster
- When the managed cluster is spamming requests to the hub cluster
Unregister from hub cluster
A recommended way to unregister a managed cluster will flip the
.spec.hubAcceptsClient bit back to false, which will be triggering the hub
control plane to offload the managed cluster from effective management.
Meanwhile, a permanent way to kick a managed cluster from the hub control plane
is simply deleting its ManagedCluster resource.
$ kubectl delete managedcluster <cluster name>
This is also revoking the previously-granted RBAC permission for the managed cluster instantly in the background. If we hope to defer the rejection to the next time when the klusterlet agent is renewing its certificate, as a minimal operation we can remove the following RBAC rules from the cluster’s effective cluster role resource:
# ClusterRole: open-cluster-management:managedcluster:<cluster name>
# Removing the following RBAC rule to stop the certificate rotation.
- apiGroups:
- register.open-cluster-management.io
resources:
- managedclusters/clientcertificates
verbs:
- renew
Unregister from the managed cluster
The admin of the managed cluster can disable the prescriptions from hub cluster
by scaling the OCM klusterlet agents to 0. Or just permanently deleting the
agent components from the managed cluster.
Managed Cluster’s certificate rotation
The certificates used by the agents from the managed cluster to talk to the hub control plane will be periodically rotated with an ephemeral and random identity. The following picture shows the automated certificate rotation works.
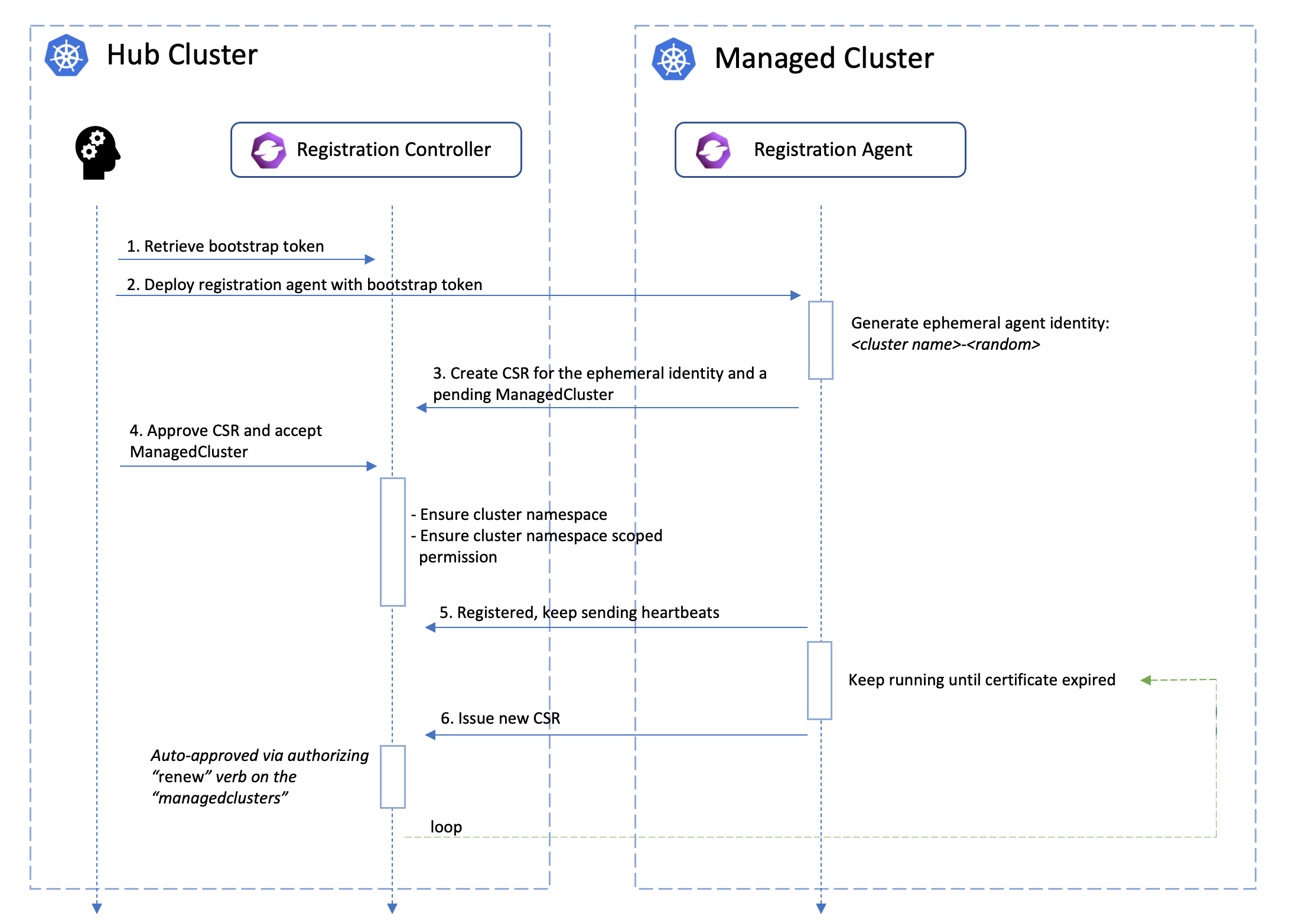
What’s next?
Furthermore, we can do advanced cluster matching/selecting within a managedclusterset using the placement module.
3 - ManagedClusterSet
API-CHANGE NOTE:
The ManagedClusterSet and ManagedClusterSetBinding API v1beta1 version will no longer be served in OCM v0.12.0.
- Migrate manifests and API clients to use the
ManagedClusterSetandManagedClusterSetBindingAPI v1beta2 version, available since OCM v0.9.0. - All existing persisted objects are accessible via the new API.
- Notable changes:
- The default cluster selector type will be
ExclusiveClusterSetLabelin v1beta2, and typeLegacyClusterSetLabelin v1beta1 is removed.
- The default cluster selector type will be
What is ManagedClusterSet?
ManagedClusterSet is a cluster-scoped API in the hub cluster for grouping a
few managed clusters into a “set” so that hub admin can operate these clusters
altogether in a higher level. The concept is inspired by the enhancement
from the Kubernetes SIG-Multicluster. Member clusters in the set are supposed
to have common/similar attributes e.g. purpose of use, deployed regions, etc.
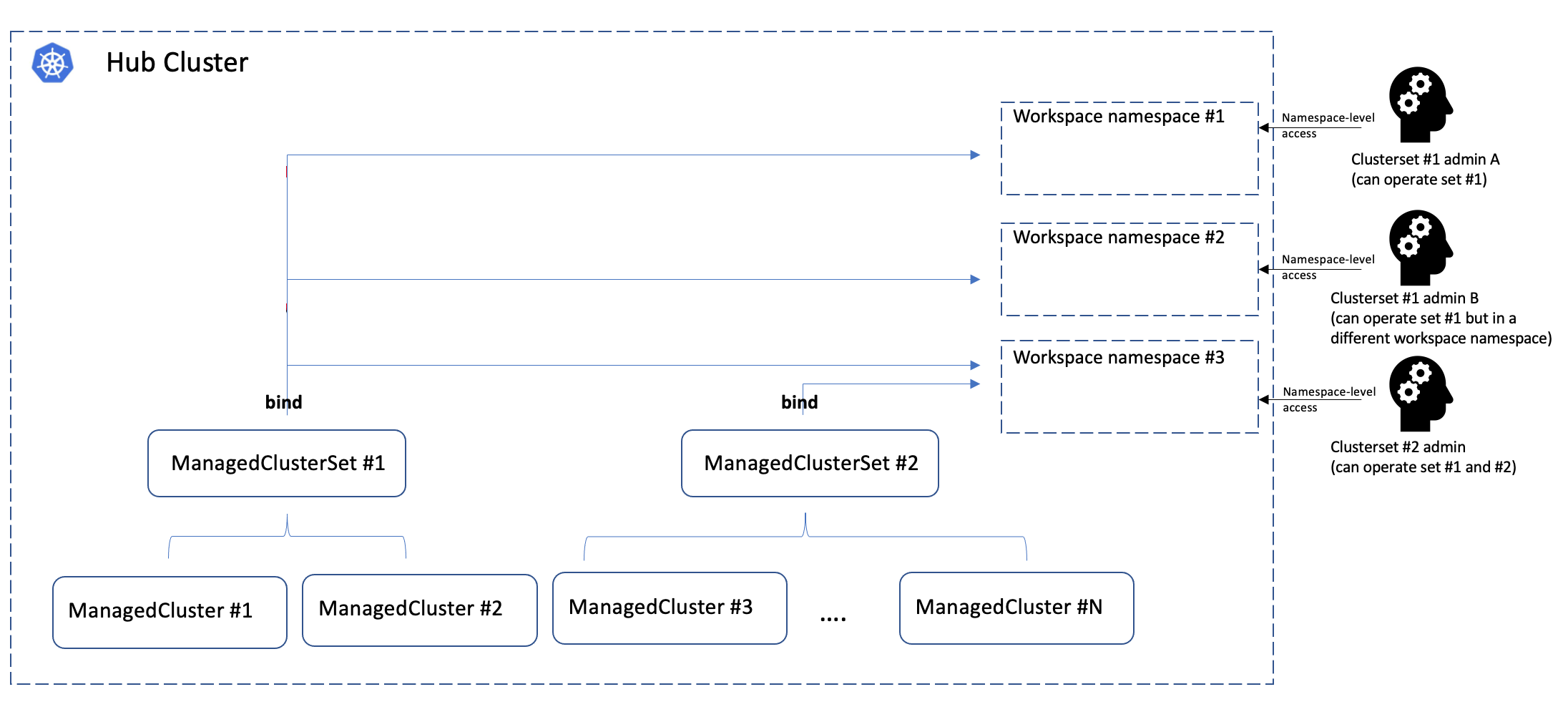
ManagedClusterSetBinding is a namespace-scoped API in the hub cluster to project
a ManagedClusterSet into a certain namespace. Each ManagedClusterSet can be
managed/administrated by different hub admins, and their RBAC permissions can
also be isolated by binding the ManagedClusterSet to a “workspace namespace” in
the hub cluster via ManagedClusterSetBinding.
Note that ManagedClusterSet and “workspace namespace” has an M*N
relationship:
- Bind multiple cluster sets to one workspace namespace indicates that the admin of that namespace can operate the member clusters from both sets.
- Bind one cluster set to multiple workspace namespace indicates that the cluster set can be operated from all the bound namespaces at the same time.
The cluster set admin can flexibly operate the member clusters in the workspace namespace using Placement API, etc.
The following picture shows the hierarchies of how the cluster set works:
Operating ManagedClusterSet using clusteradm
Creating a ManagedClusterSet
Running the following command to create an example cluster set:
$ clusteradm create clusterset example-clusterset
$ clusteradm get clustersets
<ManagedClusterSet>
└── <default>
│ ├── <BoundNamespace>
│ ├── <Status> No ManagedCluster selected
└── <example-clusterset>
│ ├── <BoundNamespace>
│ ├── <Status> No ManagedCluster selected
└── <global>
└── <BoundNamespace>
└── <Status> 1 ManagedClusters selected
The newly created cluster set will be empty by default, so we can move on adding member clusters to the set.
Adding a ManagedCluster to a ManagedClusterSet
Running the following command to add a cluster to the set:
$ clusteradm clusterset set example-clusterset --clusters managed1
$ clusteradm get clustersets
<ManagedClusterSet>
└── <default>
│ ├── <BoundNamespace>
│ ├── <Status> No ManagedCluster selected
└── <example-clusterset>
│ ├── <BoundNamespace>
│ ├── <Status> 1 ManagedClusters selected
└── <global>
└── <BoundNamespace>
└── <Status> 1 ManagedClusters selected
Note that adding a cluster to a cluster set will require the admin to have “managedclustersets/join” access in the hub cluster.
Now the cluster set contains 1 valid cluster, and in order to operate that cluster set we are supposed to bind it to an existing namespace to make it a “workspace namespace”.
Binding the ManagedClusterSet to a workspace namespace
Running the following command to bind the cluster set to a namespace. Note that the namespace SHALL NOT be an existing “cluster namespace” (i.e. the namespace has the same name of a registered managed cluster).
Note that binding a cluster set to a namespace means that granting access from that namespace to its member clusters. And the bind process requires “managedclustersets/bind” access in the hub cluster which is clarified below.
$ clusteradm clusterset bind example-clusterset --namespace default
$ clusteradm get clustersets
<ManagedClusterSet>
└── <default>
│ ├── <BoundNamespace>
│ ├── <Status> No ManagedCluster selected
└── <example-clusterset>
│ ├── <Status> 1 ManagedClusters selected
│ ├── <BoundNamespace> default
└── <global>
└── <BoundNamespace>
└── <Status> 1 ManagedClusters selected
So far we successfully created a new cluster set containing 1 cluster and bound it to a “workspace namespace”.
A glance at the “ManagedClusterSet” API
The ManagedClusterSet is a vanilla Kubernetes custom resource which can be
checked by the command kubectl get managedclusterset <cluster set name> -o yaml:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta2
kind: ManagedClusterSet
metadata:
name: example-clusterset
spec:
clusterSelector:
selectorType: ExclusiveClusterSetLabel
managedNamespaces:
- name: my-clusterset-ns1
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-02-21T09:24:38Z"
message: 1 ManagedClusters selected
reason: ClustersSelected
status: "False"
type: ClusterSetEmpty
The spec.managedNamespaces field is used to specify a list of namespaces that will be automatically created on each member cluster. For a detailed explanation, see the “Setting Managed Namespaces for a ManagedClusterSet” section below.
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta2
kind: ManagedClusterSet
metadata:
name: example-openshift-clusterset
spec:
clusterSelector:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
vendor: OpenShift
selectorType: LabelSelector
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-20T08:23:28Z"
message: 1 ManagedClusters selected
reason: ClustersSelected
status: "False"
type: ClusterSetEmpty
The ManagedClusterSetBinding can also be checked by the command
kubectl get managedclustersetbinding <cluster set name> -n <workspace-namespace> -oyaml:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta2
kind: ManagedClusterSetBinding
metadata:
name: example-clusterset
namespace: default
spec:
clusterSet: example-clusterset
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-12-19T09:55:10Z"
message: ""
reason: ClusterSetBound
status: "True"
type: Bound
Setting Managed Namespaces for a ManagedClusterSet
A ManagedClusterSet can define one or more managed namespaces. When specified, these namespaces are automatically created on every managed cluster that belongs to the set.
Example: ManagedClusterSet with managed namespaces
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta2
kind: ManagedClusterSet
metadata:
name: my-clusterset
spec:
clusterSelector:
selectorType: ExclusiveClusterSetLabel
managedNamespaces:
- name: my-clusterset-ns1
- name: my-clusterset-ns2
The managed namespaces are reflected in the status of each ManagedCluster that is part of the set.
Example: ManagedCluster status with managed namespaces
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ManagedCluster
metadata:
labels:
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/clusterset: my-clusterset
name: cluster1
status:
managedNamespaces:
- clusterSet: my-clusterset
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-09-26T03:15:52Z"
message: Namespace successfully applied and managed
reason: NamespaceApplied
status: "True"
type: NamespaceAvailable
name: my-clusterset-ns1
- clusterSet: my-clusterset
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-09-26T03:15:52Z"
message: Namespace successfully applied and managed
reason: NamespaceApplied
status: "True"
type: NamespaceAvailable
name: my-clusterset-ns2
The NamespaceAvailable condition shows whether the namespace is available on the managed cluster.
Important: Namespaces created on managed clusters are never deleted, even in the following cases:
The namespace is removed from the ManagedClusterSet specification.
The managed cluster leaves the ManagedClusterSet.
The managed cluster is detached from the hub.
Clusterset RBAC permission control
Adding member cluster to a clusterset
Adding a new member cluster to a clusterset requires RBAC permission of
updating the managed cluster and managedclustersets/join subresource. We can
manually apply the following clusterrole to allow a hub user to manipulate
that clusterset:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata: ...
rules:
- apiGroups:
- cluster.open-cluster-management.io
resources:
- managedclusters
verbs:
- update
- apiGroups:
- cluster.open-cluster-management.io
resources:
- managedclustersets/join
verbs:
- create
Binding a clusterset to a namespace
The “binding” process of a cluster set is policed by a validating webhook that
checks whether the requester has sufficient RBAC access to the
managedclustersets/bind subresource. We can also manually apply the following
clusterrole to grant a hub user the permission to bind cluster sets:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata: ...
rules:
- apiGroups:
- cluster.open-cluster-management.io
resources:
- managedclustersets/bind
verbs:
- create
Default ManagedClusterSet
For easier management, we introduce a ManagedClusterSet called default.
A default ManagedClusterSet will be automatically created initially. Any clusters not specifying a ManagedClusterSet will be added into the default.
The user can move the cluster from the default clusterset to another clusterset using the command:
clusteradm clusterset set target-clusterset --clusters cluster-name
default clusterset is an alpha feature that can be disabled by disabling the feature gate in registration controller as:
- "--feature-gates=DefaultClusterSet=false"
Global ManagedClusterSet
For easier management, we also introduce a ManagedClusterSet called global.
A global ManagedClusterSet will be automatically created initially. The global ManagedClusterSet include all ManagedClusters.
global clusterset is an alpha feature that can be disabled by disabling the feature gate in registration controller as:
- "--feature-gates=DefaultClusterSet=false"
global ManagedClusterSet detail:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta2
kind: ManagedClusterSet
metadata:
name: global
spec:
clusterSelector:
labelSelector: {}
selectorType: LabelSelector
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-06-20T08:23:28Z"
message: 1 ManagedClusters selected
reason: ClustersSelected
status: "False"
type: ClusterSetEmpty